上一篇文章我们介绍了如何使用默认规则做条件下推,今天我们来尝试自定义规则,来实现对SQL的重写。Select * from consumers 实际查询则为 Select * from consumers_1,这个需求在分库分表里应该也很常见了。
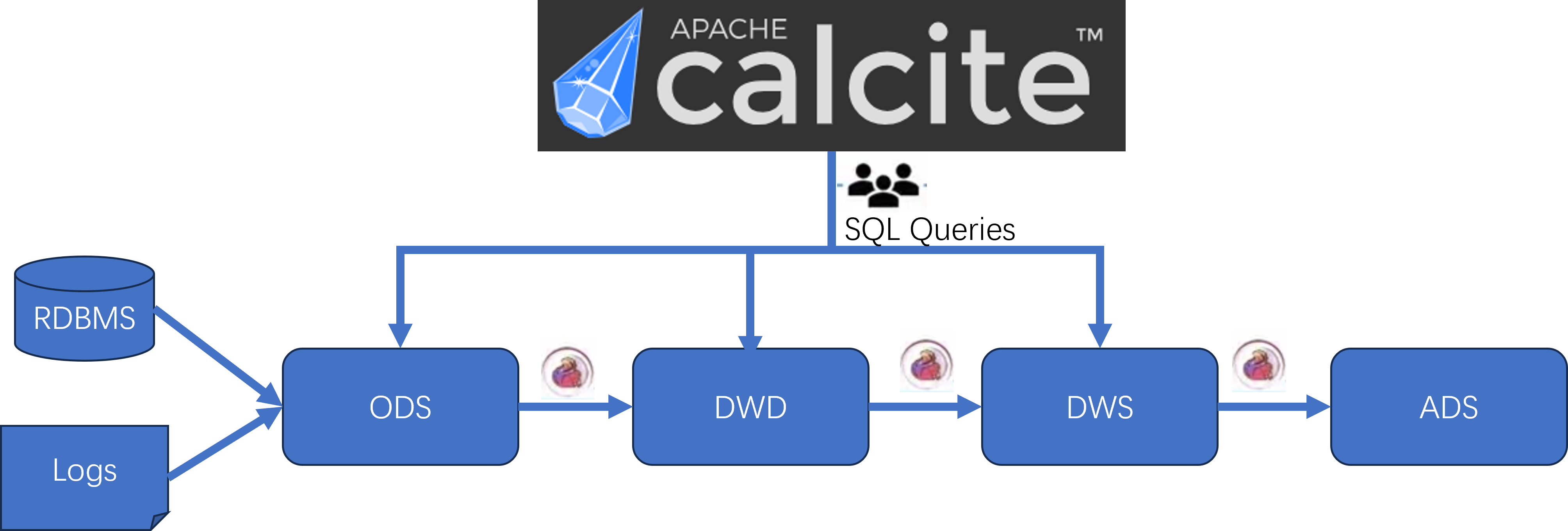
湖仓一体 数据仓库 数据仓库是一个面向主题的、集成的、相对稳定的、反映历史变化的数据存储系统,它主要存储的是结构化数据,历史数据通过抽取、转换、整合以及清理,并导入到目标表中,主要用于业务决策分析。
随着当前大量信息化发展和电子设备产品普及,产生大量的照片、视频、文档等非结构化数据,人们也想通过大数据技术找到这些数据的关系,所以设计了一个比数据仓库还要大的系统,可以把非结构化和结构化数据共同存储和做一些处理,这个系统叫做数据湖。
数据湖 数据湖是一个以原始格式存储数据的存储库或系统,它按原样存储数据,而无需事先对数据进行结构化处理,可以存储结构化数据(如关系型数据库中的表),半结构化数据(如CSV、日志、XML、JSON),非结构化数据(如电子邮件、文档、PDF)和二进制数据(如图片、音频、视频),以供机器学习、深度学习、统计分析等多种形式数据分析应用。
数据湖开放的数据存储结构给数据入湖带来了更大的灵活性,各种结构化、半结构化、非结构化的原始数据可以直接入湖。另外,开放存储给上层的计算引擎也带来了更多的灵活度,各种计算引擎需要遵循相当宽松的兼容性约定即可根据自己针对的场景随意读写数据湖中的数据。而数据仓库则更关注数据使用效率、数据的安全性和数据治理能力,这对企业的长远的成长性发展至关重要。
湖仓一体 湖仓一体是一种新型开放式架构,将数据湖和数据仓库的优势充分结合,它构建在数据湖低成本的数据存储架构之上,又继承了数据仓库的数据处理和管理功能。湖仓一体打通数据湖和数据仓库两套体系,让数据和计算在湖和仓之间自由流动,更能发挥出数据湖的灵活性,以及数据数据仓库的成长性。
但是湖仓一体≠数据湖+数据仓库,湖仓一体不等同于数据湖和数据仓简单打通,湖仓一体的构建需要解决以下三个关键问题:
湖和仓的数据/元数据在不需要用户人工干预的情况下,可以无缝打通、自由顺畅地流动;
系统根据特定的规则自动地将数据在湖仓之间进行缓存和移动,根据规则自动决定哪些数据放在数仓,哪些保留在数据湖,进而形成一体化;
湖和仓有统一的开发体验,存储在不同系统的数据,可以通过一个统一的开发/管理平台操作。
以上内容引用自:湖仓一体数据平台架构
上图是我设想的一种湖仓一体架构,JimSQL 可以考虑支持这种架构了。 夹带一个私货 JimSql = Jim Isn’t MySQL. Jim is a filesystem database system implemention use Java. 笔者开源的一个数据库,目前正在使用 bitcask 升级存储系统,欢迎有兴趣的小伙伴一起搞起来呀!
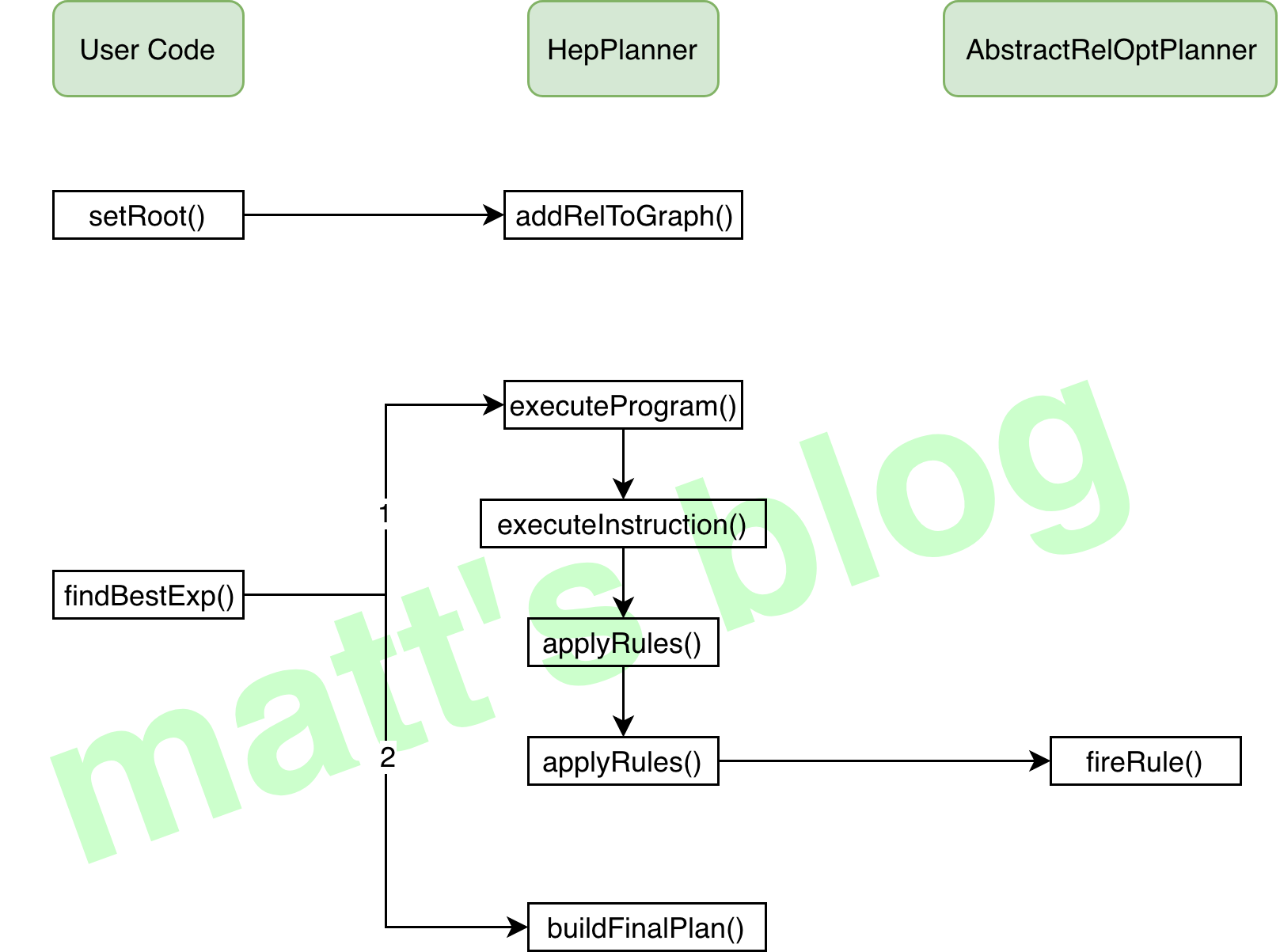
执行流程 我们再来复习一下执行流程,借用 柳年思水 大佬的图,HepPlanner 在优化过程中,是先遍历规则,然后再对每个节点进行匹配转换,直到满足条件(超过限制次数或者规则遍历完一遍不会再有新的变化)
准备数据 首先我们先准备数据,延用我们一直的案例,将consumers.csv再复制一份consumers_1.csv并修改里面的记录,用于区分效果。
consumers.csv 1 2 3 4 id,firstname,lastname,birth 1,li,jacky,1984 2,li,doudou,2019 3,li,maimai,2019
consumers_1.csv 1 2 3 4 id,firstname,lastname,birth 1,liu,jacky,1984 2,liu,doudou,2019 3,liu,maimai,2019
自定义规则 根据我们的需求,实际上只需要在扫描表的适合,对应的将源表替换为目标表即可,onMatch(final RelOptRuleCall call)方法里,匹配到映射关系,将源表替换成重新生成的RelNode
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 TableScan tableScan = call.rel(0 );for (String tn : tableScan.getTable().getQualifiedName()){ if (srcName.equals(tn)){ RelBuilder relBuilder = RelBuilder.create(frameworkConfig); RelNode relNode = relBuilder.scan(targetName).build(); call.transformTo(relNode); } }
构建配置的匹配规则
1 2 3 4 5 default JackyTableRenameRule.Config withOperandFor (Class<? extends TableScan> tableScanClass) { return withOperandSupplier(b0 -> b0.operand(tableScanClass).anyInputs()) .as(JackyTableRenameRule.Config.class); }
以下是完整代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 package com.dafei1288;import org.apache.calcite.plan.RelOptRuleCall;import org.apache.calcite.plan.RelRule;import org.apache.calcite.rel.RelNode;import org.apache.calcite.rel.core.TableScan;import org.apache.calcite.rel.rules.*;import org.apache.calcite.tools.FrameworkConfig;import org.apache.calcite.tools.RelBuilder;import org.apache.calcite.tools.RelBuilderFactory;import org.immutables.value.Value;@Value .Enclosingpublic class JackyTableRenameRule extends RelRule <JackyTableRenameRule.Config> implements TransformationRule { private String srcName; private String targetName; private FrameworkConfig frameworkConfig; public String getSrcName () { return srcName; } public void setSrcName (String srcName) { this .srcName = srcName; } public String getTargetName () { return targetName; } public void setTargetName (String targetName) { this .targetName = targetName; } public FrameworkConfig getFrameworkConfig () { return frameworkConfig; } public void setFrameworkConfig (FrameworkConfig frameworkConfig) { this .frameworkConfig = frameworkConfig; } protected JackyTableRenameRule (Config config) { super ( config ); } @Deprecated public JackyTableRenameRule (RelBuilderFactory relBuilderFactory) { this (JackyTableRenameRule.Config.DEFAULT.withRelBuilderFactory(relBuilderFactory) .as(JackyTableRenameRule.Config.class)); } @Override public void onMatch (final RelOptRuleCall call) { TableScan tableScan = call.rel(0 ); for (String tn : tableScan.getTable().getQualifiedName()){ if (srcName.equals(tn)){ RelBuilder relBuilder = RelBuilder.create(frameworkConfig); RelNode relNode = relBuilder.scan(targetName).build(); call.transformTo(relNode); } } } @Value .Immutable public interface Config extends RelRule .Config { static Config DEFAULT = ImmutableJackyTableRenameRule.Config.builder().build().withOperandFor(TableScan.class); @Override default JackyTableRenameRule toRule () { return new JackyTableRenameRule (this ); } default JackyTableRenameRule toRule (String srcName, String targetName) { JackyTableRenameRule jtrr = new JackyTableRenameRule (this ); jtrr.setSrcName(srcName); jtrr.setTargetName(targetName); return jtrr; } @Value .Default default boolean isAllowAlwaysTrueCondition () { return true ; } default JackyTableRenameRule.Config withOperandFor (Class<? extends TableScan> tableScanClass) { return withOperandSupplier(b0 -> b0.operand(tableScanClass).anyInputs()) .as(JackyTableRenameRule.Config.class); } } }
测试代码 下面是实例化规则,并加入优化代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 HepProgramBuilder hepProgramBuilder = HepProgram.builder();JackyTableRenameRule jtrr = JackyTableRenameRule.Config.DEFAULT.toRule("consumers" ,"consumers_1" );jtrr.setFrameworkConfig(frameworkConfig); hepProgramBuilder.addRuleInstance(jtrr); HepProgram program = hepProgramBuilder.build();HepPlanner hepPlanner = new HepPlanner (program);hepPlanner.setRoot(opTree); RelNode r = hepPlanner.findBestExp();
完整测试代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 package com.dafei1288;import org.apache.calcite.adapter.csv.CsvSchema;import org.apache.calcite.adapter.csv.CsvTable;import org.apache.calcite.plan.RelOptUtil;import org.apache.calcite.plan.hep.HepPlanner;import org.apache.calcite.plan.hep.HepProgram;import org.apache.calcite.plan.hep.HepProgramBuilder;import org.apache.calcite.rel.RelNode;import org.apache.calcite.rel.RelWriter;import org.apache.calcite.rel.core.JoinRelType;import org.apache.calcite.rel.externalize.RelWriterImpl;import org.apache.calcite.rel.rules.FilterJoinRule;import org.apache.calcite.schema.SchemaPlus;import org.apache.calcite.sql.fun.SqlStdOperatorTable;import org.apache.calcite.sql.parser.SqlParser;import org.apache.calcite.tools.FrameworkConfig;import org.apache.calcite.tools.Frameworks;import org.apache.calcite.tools.RelBuilder;import org.apache.calcite.tools.RelRunners;import java.io.File;import java.io.PrintWriter;import java.sql.ResultSet;public class JackSqlRewriteCase { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { SchemaPlus rootSchema = Frameworks.createRootSchema(true ); String csvPath = "src\\main\\resources\\db" ; CsvSchema csvSchema = new CsvSchema (new File (csvPath), CsvTable.Flavor.SCANNABLE); rootSchema.add("consumers" , csvSchema.getTable("consumers" )); rootSchema.add("consumers_1" , csvSchema.getTable("consumers_1" )); rootSchema.add("orders" , csvSchema.getTable("orders" )); FrameworkConfig frameworkConfig = Frameworks.newConfigBuilder() .parserConfig(SqlParser.Config.DEFAULT) .defaultSchema(rootSchema) .build(); RelBuilder relBuilder = RelBuilder.create(frameworkConfig); RelNode cnode = relBuilder.scan("consumers" ).build(); System.out.println("==> " + RelOptUtil.toString(cnode)); cnode = relBuilder.scan("consumers" ).project(relBuilder.field("firstname" ), relBuilder.field("lastname" )).build(); System.out.println("==> " +RelOptUtil.toString(cnode)); RelNode opTree = relBuilder .scan("consumers" ) .project( relBuilder.field("id" ), relBuilder.field("firstname" ), relBuilder.field("lastname" )) .build(); RelWriter rw = new RelWriterImpl (new PrintWriter (System.out, true )); opTree.explain(rw); System.out.println(); HepProgramBuilder hepProgramBuilder = HepProgram.builder(); JackyTableRenameRule jtrr = JackyTableRenameRule.Config.DEFAULT.toRule("consumers" ,"consumers_1" ); jtrr.setFrameworkConfig(frameworkConfig); hepProgramBuilder.addRuleInstance(jtrr); HepProgram program = hepProgramBuilder.build(); HepPlanner hepPlanner = new HepPlanner (program); hepPlanner.setRoot(opTree); RelNode r = hepPlanner.findBestExp(); r.explain(rw); System.out.println(); ResultSet result = RelRunners.run(r).executeQuery(); int columns = result.getMetaData().getColumnCount(); while (result.next()) { System.out.println(result.getString(1 ) + " " + result.getString(2 ) + " " + result.getString(3 )); } } }
结果展示 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ==> LogicalTableScan(table=[[consumers]]) ==> LogicalProject(firstname=[$1], lastname=[$2]) LogicalTableScan(table=[[consumers]]) 4:LogicalProject(id=[$0], firstname=[$1], lastname=[$2]) 3:LogicalTableScan(table=[[consumers]]) 6:LogicalProject(id=[$0], firstname=[$1], lastname=[$2]) 8:LogicalTableScan(table=[[consumers_1]]) 1 liu jacky 2 liu doudou 3 liu maimai Process finished with exit code 0
可以通过执行计划看到 LogicalTableScan 由 consumers
1 2 4:LogicalProject(id=[$0], firstname=[$1], lastname=[$2]) 3:LogicalTableScan(table=[[consumers]])
转变到了 consumers_1
1 2 6:LogicalProject(id=[$0], firstname=[$1], lastname=[$2]) 8:LogicalTableScan(table=[[consumers_1]])
查询出来的数据,也证明了执行计划的变更。
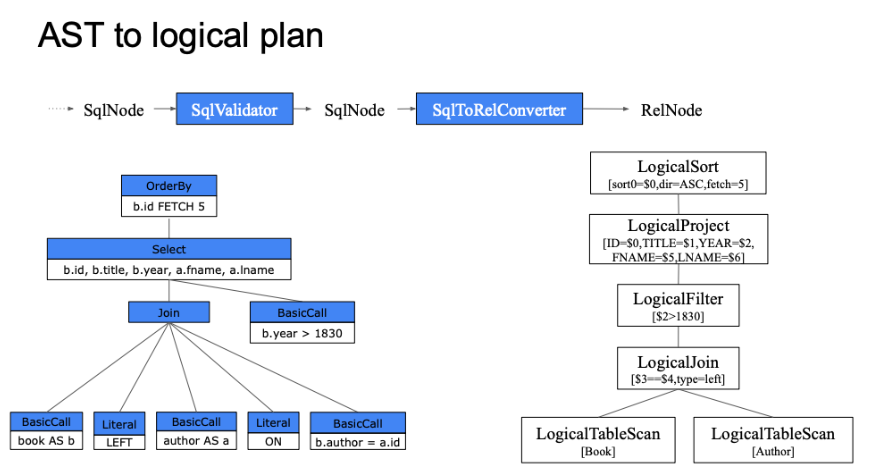
SqlNode RelNode RexNode 首先我们补充一下,对SqlNode、RelNode、RexNode的理解
SqlNode 是 Parse、Validate 阶段的结果,对应 SQL 转换为语法树后的每个节点,例如 SqlSelect SqlJoin.
RelNode 是 SqlToRelConverter、Optimize 阶段的结果,对应语法树转换为关系运算符的节点,例如 LogicalProject LogicalJoin,这些节点操作的都是集合,是关系代数运算符的一种,即 relational expression.
RexNode 跟 RelNode 位于同一阶段,操作的是数据本身,例如limit 5里的 5 是RexLiteral,b.publish_year > 1830、b.author_id = a.id都是RexCall,对应常量、函数的表达式,即 Expression Node.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 SqlNode is the abstract syntax tree that represents the actual structure of the query a user input. When a query is first parsed, it's parsed into a SqlNode. For example, a SELECT query will be parsed into a SqlSelect with a list of fields, a table, a join, etc. Calcite is also capable of generating a query string from a SqlNode as well. RelNode represents a relational expression - hence "rel." RelNodes are used in the optimizer to decide how to execute a query. Examples of relational expressions are join, filter, aggregate, etc. Typically, specific implementations of RelNode will be created by users of Calcite to represent the execution of some expression in their system. When a query is first converted from SqlNode to RelNode, it will be made up of logical nodes like LogicalProject, LogicalJoin, etc. Optimizer rules are then used to convert from those logical nodes to physical ones like JdbcJoin, SparkJoin, CassandraJoin, or whatever the system requires. Traits and conventions are used by the optimizer to determine the set of rules to apply and the desired outcome, but you didn't ask about conventions :-) RexNode represents a row expression - hence "Rex" - that's typically contained within a RelNode. The row expression contains operations performed on a single row. For example, a Project will contain a list of RexNodes that represent the projection's fields. A RexNode might be a reference to a field from an input to the RedNode, a function call (RexCall), a window (RexOver), etc. The operator within the RexCall defines what the node does, and operands define arguments to the operator. For example, 1 + 1 would be represented as a RexCall where the operator is + and the operands are 1 and 1. What RelNode and RexNode together give you is a way to plan and implement a query. Systems typically use VolcanoPlanner (cost-based) or HepPlanner (heuristic) to convert the logical plan (RelNode) into a physical plan and then implement the plan by converting each RelNode and RexNode into whatever is required by the system for which the plan is generated. The optimizer might push down or pull up expressions or reorder joins to create a more optimal plan. Then, to implement that plan, e.g. the JDBC integration will convert an optimized RelNode back into a SqlNode and then a query string to be executed against some database over JDBC. The Spark implementation will convert RelNodes into operations on a Spark RDD. The Cassandra implementation will generate a CQL query, etc.
参考连接 https://lists.apache.org/thread/z3pvzy1fnl6t5m04gd3wv4tntwpf3g52
https://izualzhy.cn/calcite-example
http://matt33.com/2019/03/17/apache-calcite-planner/
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/61661909
https://blog.csdn.net/u010022051/article/details/125609517